Understanding Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT): A Path to Emotional Wellness
Written by Aimee Oliveri (Clinical Psychologist, dialectical behavior therapy therapist, Mental Health Content Creator) in Collaboration with Clarity Health Care
On the path to emotional wellness and mental health, it's crucial to explore the different therapeutic approaches available. One approach that has gained recognition for its effectiveness is Dialectical Behaviour Therapy, commonly referred to as DBT. This article will delve into DBT and how it can be a valuable tool for achieving emotional well-being.
What is Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT)?
Dialectical Behaviour Therapy, or DBT for short, is a widely recognised and evidence-based approach developed by Marsha Linehan, to help individuals struggling with emotional regulation, particularly those with borderline personality disorder (BPD). DBT has since been shown to be effective for a wide range of mental health challenges, including depression, anxiety, eating disorders, PTSD, and maladaptive behaviours such as self-harm and substance misuse.
The general goal of Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) is to build a life worth living, by building healthier coping mechanisms, and utilising skills to navigate challenging situations, emotions, and relationships more effectively.
What are Dialectics?
In the context of DBT, dialectics refers to the idea that two seemingly opposite or conflicting things can be true at the same time. It recognises that multiple truths or perspectives can exist simultaneously and that finding a balance or synthesis between these opposing elements is beneficial for emotional well-being.
Dialectical thinking is the opposite of absolutist or black and white thinking.
For example:
I can love someone deeply AND I can let them go
I am doing the best I can AND I can do better
I am independent AND I need help
I can disagree with the rules AND follow the rules
I can be mad at someone AND love and respect them
The Core Dialectic of DBT - Balancing Acceptance and Change
The foundation of DBT is the dialectic that acceptance and change can co-exist.
For example:
Learning to balance acceptance of ourselves exactly the way we are in this moment with intense efforts to improve our lives.
Learning to recognise the elements of situations we can change, and the elements that are out of our control, thus requiring acceptance.
Emotional Regulation Difficulties Vs Pervasive Emotional Dysregulation
There are three components to emotion regulation:
Reactivity: how quickly we react emotionally to a situation
Duration: how long the emotional response lasts
Intensity: how intense the emotion gets
People who struggle with emotion regulation difficulties, may struggle with one or more of these components from time to time due to a variety of reasons, like ADHD or high amounts of stress. See graph below for a visual representation:
(Gross & Jazaieri, 2014)
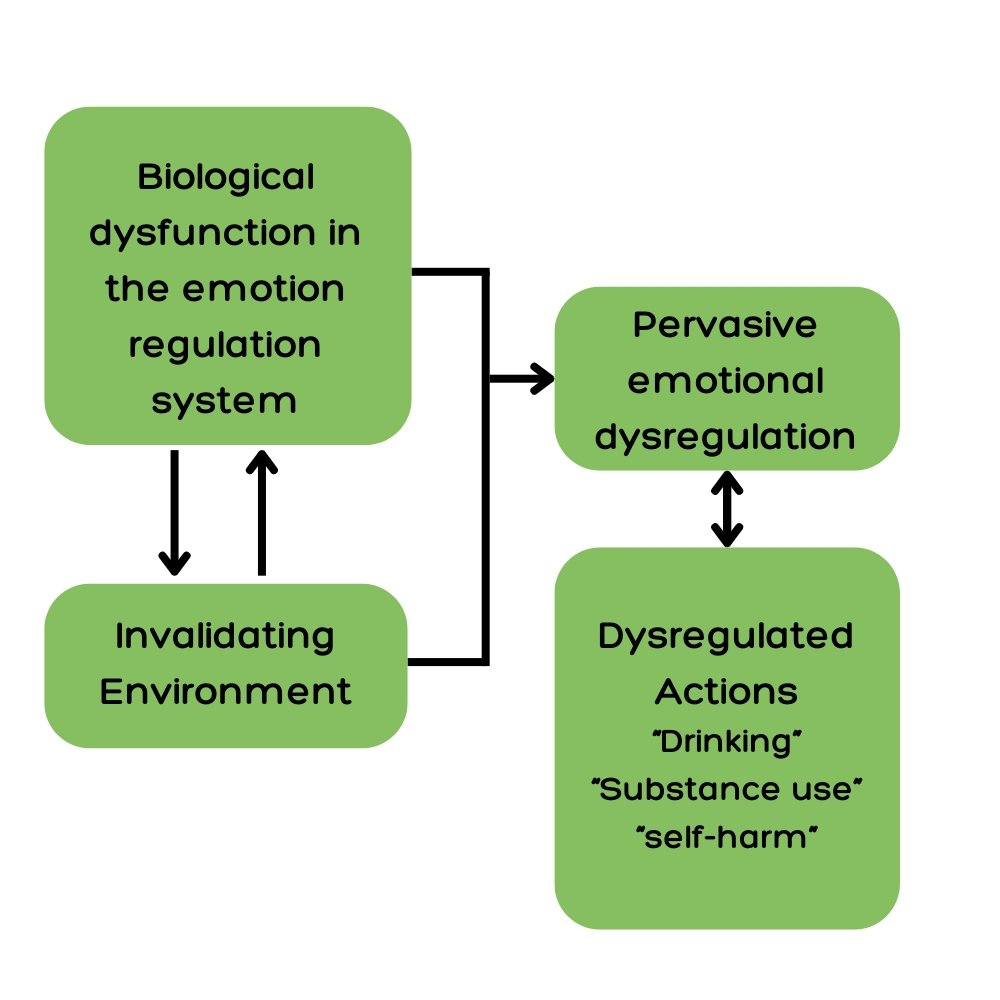
Pervasive emotion dysregulation, on the other hand, occurs when an individual does not acquire emotion regulation skills during their up brining for a myriad of reasons such as an invalidating environment. Consequently, they may turn to coping behaviours like drinking or self-harm, in an effort to manage their emotions. However, in the long-term, these coping mechanisms maintain unhelpful coping and a continued struggle with emotional dysregulation. See image below for a visual representation:
Transactional Model of BPD (Linehan et al., 1993)
DBT in Action - The Four Key Modules of DBT
DBT is structured into four key modules:
Mindfulness: Mindfulness is the foundation of DBT. It involves being fully present in the moment, observing your thoughts and emotions without judgment. Mindfulness practices help you become more aware of your emotional experiences and reduce reactivity.
Distress Tolerance: This module focuses on developing healthy coping strategies for handling emotional crises. It equips individuals with tools to tolerate distressing situations without resorting to maladaptive coping behaviours.
Emotion Regulation: Emotion regulation helps people identify and label their emotions and assists them in learning skills for regulating their emotions effectively.
Interpersonal Effectiveness: This module teaches effective communication and relationship skills. It provides guidance on asserting needs and boundaries while maintaining positive and healthy relationships.
The mindfulness and distress tolerance modules focus on building acceptance skills, while the emotion regulation and interpersonal effectiveness modules focus on building change skills.
Note: dialectical behavior therapy therapists recommend DBT to be delivered as a Group Therapy program, alongside individual treatment.
Benefits of DBT
DBT isn't just about addressing specific mental health issues; it's also about enhancing overall emotional well-being. By becoming more mindful of your emotions, learning to cope with distress, regulating your emotional responses, and improving your interpersonal skills, you can make positive changes in your life.
Here are some benefits of DBT:
Increased self-awareness: DBT encourages you to improve self-awareness, promoting self-understanding and personal growth.
Better coping mechanisms: You'll acquire effective strategies to manage emotional crises and navigate challenging situations.
Improved relationships: By enhancing interpersonal effectiveness, you can foster healthier connections with others.
Reduced maladaptive coping: DBT equips you with the tools to replace maladaptive coping with healthier alternatives.
Greater emotional stability: The skills learned in DBT can lead to a more stable and balanced emotional life.
Summing Up
Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) is a powerful approach for building a life worth living. It focuses on accepting and regulating emotions while promoting positive changes in behaviour and thinking patterns. Whether you're dealing with emotional dysregulation, or simply seeking to enhance your emotional wellness, DBT is beneficial.
If you want to explore the benefits of DBT, our team of mental health clinicians at Clarity Health Care are well-versed in DBT and can assist you in understanding and applying these valuable skills to your life.
DBT Therapy near you? Please contact Clarity Health Care here for guidance on booking an appointment with one of our dialectical behavior therapy therapists.
The key clinical interventions that our Psychologists, Clinical Psychologists, and Psychiatrists use are:
Eye Movement Desensitisation & Reprocessing (EMDR Therapy)
Acceptance Commitment Therapy (ACT)
Schema Therapy
Motivational Interviewing
Family and Couples Therapy
Pharmacological Therapy
Emotion dysregulation graph - https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Important-factors-in-emotion-dysregulation-as-a-function-of-intensity-and-time_fig2_275594654